Habitat Loss: Understanding the Crisis Threatening Global Wildlife
Around the world, ecosystems are changing faster than ever before. Forests shrink, wetlands dry up, coral reefs fade, and grasslands turn into farmland or urban developments. These dramatic transformations are responsible for one of the most urgent environmental challenges of our time: Habitat Loss.
When natural environments disappear or become too degraded to support life, species struggle to survive. Populations decline, migration routes break, and food chains collapse. Understanding Habitat Loss is essential not only for wildlife preservation but for human wellbeing, as healthy ecosystems support clean air, water, and a stable climate.
What Habitat Loss Really Means
The term Habitat Loss refers to the destruction, fragmentation, or degradation of environments that species depend on. This can occur through deforestation, mining, agriculture, urban expansion, pollution, and climate change.
When habitats disappear, animals lose shelter, food sources, breeding spaces, and migration paths. Plants lose the soil and climate conditions they require. Even slight changes in water availability or temperature can make an area unlivable for sensitive species.
This crisis doesn’t affect only rare animals; it impacts insects, birds, fish, mammals, and plants that form the foundation of life on Earth.
The Major Causes Behind Habitat Loss
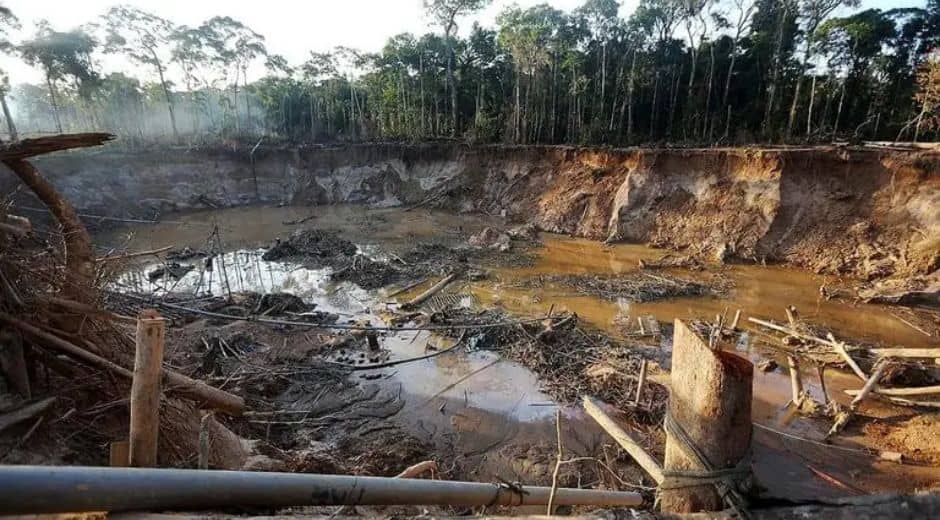
Human activity drives most environmental declines. Expanding cities replace forests with concrete; industrial farming clears land at massive scale; mining strips soil of nutrients; pollution poisons rivers and oceans.
Climate change accelerates the problem, pushing habitats beyond their natural limits. Rising temperatures, severe storms, and prolonged droughts permanently alter environments.
Reports from WWF highlight the enormous role that agriculture plays, accounting for the majority of global land conversion. As the human population grows, so does the pressure on ecosystems.
How Habitat Loss Impacts Wildlife
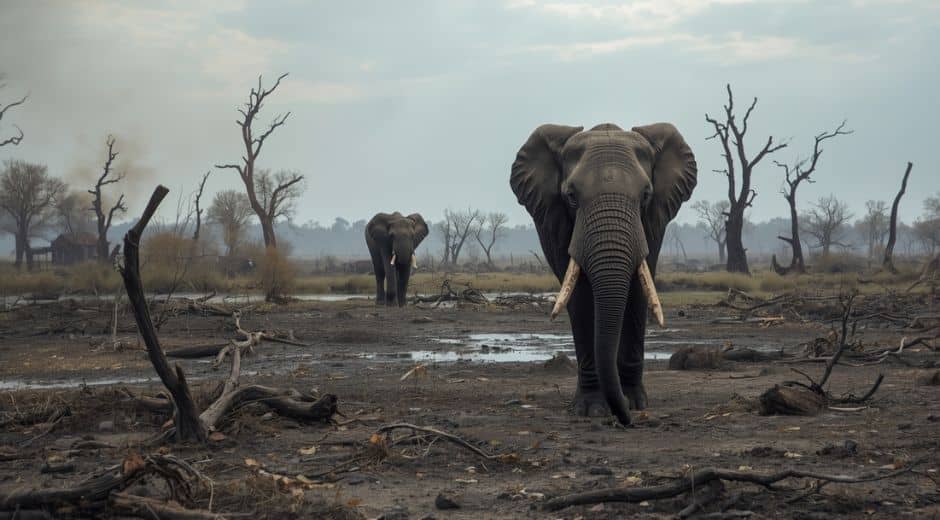
Wildlife suffers immediately when environments disappear. Animals may be pushed into unfamiliar areas where they cannot find food or shelter. Predators lose their hunting grounds; herbivores lose vegetation; birds lose nesting areas.
For many species, even a minor disturbance can disrupt survival. Amphibians depend on moist environments, bees rely on diverse flowers, and large mammals require vast territories. Habitat Loss removes the resources they rely on, leading to population decline or extinction.
In fragmented ecosystems, animals struggle to travel between safe zones, making mating and migration difficult.
Habitat Loss and Biodiversity Decline
Ecosystems require balance to stay healthy. When plants and animals disappear, the entire system weakens. Biodiversity declines, and the environment loses resilience.
Without pollinators, crops fail. Without predators, prey overpopulate and deplete vegetation. Without plant diversity, soil becomes infertile.
This chain reaction shows why Habitat Loss is considered one of the greatest threats to global biodiversity. The disappearance of even one species can destabilize entire regions.
Human Consequences of Habitat Loss
The impacts reach far beyond wildlife. Humans depend on natural environments for water filtration, climate regulation, fertile soil, and flood control. Forests absorb carbon dioxide, wetlands store water, and grasslands support pollinators essential for food production.
When Habitat Loss accelerates, communities face droughts, food shortages, storms, and rising temperatures. Coastal areas become more vulnerable to flooding as protective mangroves and coral reefs disappear.
The economic consequences are massive. Agriculture, tourism, and fishing industries all suffer when natural areas degrade.
Habitat Loss and Climate Change: A Dangerous Cycle
Climate change and Habitat Loss feed into each other, creating a dangerous cycle. When forests are destroyed, carbon dioxide is released, contributing to warming. As warming intensifies, ecosystems become more fragile and vulnerable.
Coral reefs bleach under rising temperatures, Arctic ice melts, and rainforests become drier. These changes further damage habitats, leading to species decline.
Scientists warn that protecting ecosystems is one of the most effective strategies for slowing global warming.
Efforts to Combat Habitat Loss
Conservation groups, governments, and communities across the world are working to reverse this crisis. Protected areas such as national parks safeguard critical ecosystems. Reforestation projects restore damaged landscapes. Wildlife corridors reconnect fragmented habitats.
Marine sanctuaries protect coral reefs and fish populations, while wetlands restoration improves water quality and biodiversity.
You can explore innovative environmental projects on platforms like FinanceWorldHub, where sustainability-focused technologies are highlighted.
Community-Based Conservation
Local communities play an essential role. Indigenous groups, farmers, fishers, and residents often protect their land through traditional practices. When supported, these communities become powerful allies in preventing Habitat Loss.
Education and sustainable development programs empower people to use land responsibly, benefiting both nature and local economies.
When communities are involved, conservation becomes long-lasting and meaningful.
Habitat Restoration Projects Around the World
Successful restoration efforts offer hope. Rewilding initiatives reintroduce native species and rebuild ecological processes. Forest restoration programs plant native trees, while river restoration removes dams and allows fish to return to their natural paths.
In some regions, abandoned farmland is converted back into natural landscapes, welcoming wildlife that vanished decades ago.
Restoration doesn’t just rebuild nature — it strengthens climate resilience and improves human living conditions.
The Role of Technology in Protecting Habitats
Technology enhances conservation work through satellite tracking, AI analysis, and drone mapping. Scientists can monitor deforestation, track species movement, and predict environmental changes with unprecedented accuracy.
Crowdsourcing apps allow citizens to report illegal logging or document endangered species. Public participation combined with scientific tools makes conservation more effective.
These innovations help prevent Habitat Loss before it becomes irreversible.
How Individuals Can Help Prevent Habitat Loss
Even small actions contribute to global change. People can support eco-friendly businesses, reduce waste, plant native species, and protect pollinators.
Avoiding products linked to deforestation, such as unsustainable palm oil or illegal timber, makes a significant impact. Supporting conservation charities or participating in local environmental cleanups strengthens global efforts.
Every choice influences the demand for land, water, and energy.
Internal Connection: Protecting the Balance of Nature
At BioNatureVista, we explore the environmental challenges shaping our world. Habitat Loss stands as one of the most urgent issues affecting wildlife, ecosystems, and future generations.
Understanding this crisis encourages meaningful action and highlights the importance of protecting natural spaces before they disappear.
Conservation is not just about ecosystems — it’s about safeguarding life itself.
Conclusion: A Race to Protect What Remains
The fight against Habitat Loss defines the future of the planet. Every species, from the smallest insect to the largest predator, depends on healthy environments for survival.
Protecting these spaces ensures biodiversity, climate stability, clean water, and a sustainable future for humanity.
The solutions exist, and they begin with awareness, cooperation, and action. By valuing natural habitats, supporting conservation, and advocating for responsible development, we help secure a world where wildlife and people can thrive together.
The time to act is now, before more ecosystems vanish forever.
Nature Inspires Every Step

Canopy Stratification and the Hidden Layers of Forest Life
Canopy Stratification and the Hidden Layers of Forest Life

Understanding Natural Systems And Their Interconnections
Understanding Natural Systems And Their Interconnections