Air Quality: How to Understand and Improve the Air Around You
What is air quality
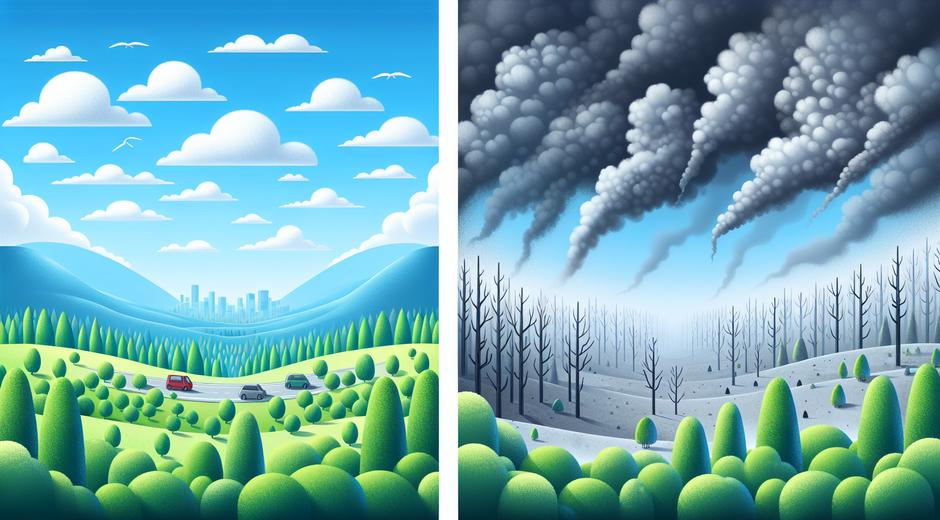
Air quality refers to the condition of the air we breathe in relation to how clean or polluted it is. Good air quality supports health and vibrant ecosystems. Poor air quality contains contaminants that can harm human health, stress plants and animals, and degrade natural habitats. Many factors influence air quality including emissions from vehicles and industry, natural wildfires, weather patterns and indoor sources such as cooking and cleaning products.
Common air pollutants and what they mean
Understanding the main pollutants helps people take targeted action. Particulate matter is often listed as PM2.5 and PM10. These particles vary in size and can penetrate lungs and enter the bloodstream. Ground level ozone forms when pollutants from cars and factories react with sunlight. Nitrogen dioxide and sulfur dioxide come from combustion processes and can irritate airways. Volatile organic compounds are emitted from paints cleaning agents and fuels and may cause short term symptoms and long term risks. Carbon monoxide is produced by incomplete combustion and is dangerous because it reduces oxygen delivery in the body.
How poor air quality affects health and nature
Exposure to poor air quality can cause immediate symptoms such as coughing watery eyes and headaches. Over time repeated exposure may increase the risk of respiratory diseases heart disease and some cancers. Children older adults and people with pre existing respiratory conditions are especially vulnerable. Beyond human health air pollution harms plants by reducing photosynthesis and increasing susceptibility to pests and disease. Soil and water quality can also deteriorate when pollutants settle out of the atmosphere impacting entire ecosystems.
Indoor air quality versus outdoor air quality
Many people assume indoor air is always safer. In some cases indoor air concentrates pollutants due to limited ventilation and continuous emission sources. Common indoor contributors include tobacco smoke cooking emissions mold and chemical products. Outdoor air quality fluctuates with traffic patterns industrial activity weather and seasonal events like wildfires. Improving ventilation controlling sources and using filtration can greatly improve indoor air. Checking local outdoor air quality indexes before planning exercise or outdoor activities can protect health on poor air days.
How air quality is measured and monitored
Air quality monitoring ranges from national networks to community sensors and personal monitors. Official systems measure a suite of pollutants and report an air quality index that simplifies complex data into easy to understand categories. Small sensors and citizen science projects expand coverage and raise awareness though they vary in accuracy. Satellite observations give a broad view and help track large scale events like dust storms or fires. Regular monitoring informs policy and lets communities respond to urgent conditions with timely guidance.
Technology and nature based solutions to improve air quality
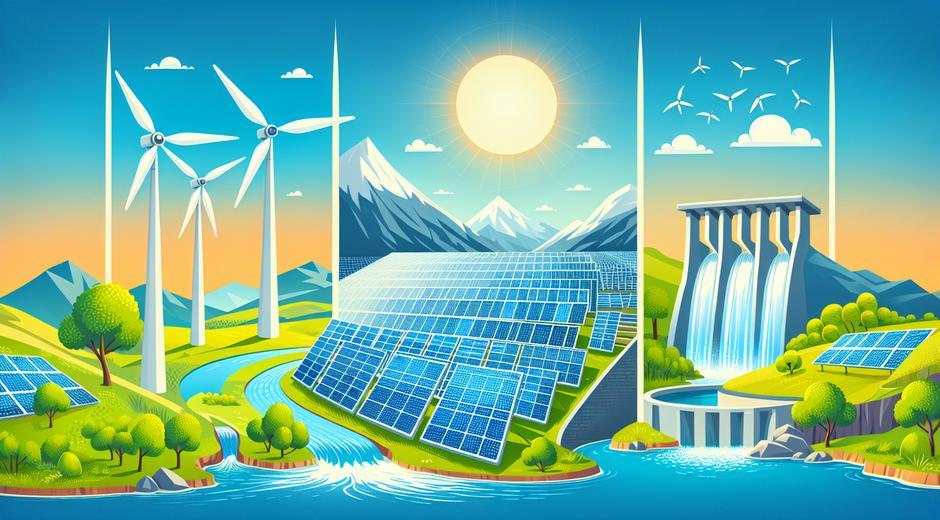
Many solutions combine technology and nature. Cleaner vehicle engines and electric vehicles reduce tailpipe emissions. Industrial controls and cleaner fuels cut emissions at the source. Urban planning that reduces car dependence and adds green corridors helps filter pollutants and cool city temperatures. Trees and vegetation capture particles and absorb gases. Green infrastructure like bioswales and permeable surfaces reduces runoff and supports healthy urban ecosystems. Simple household improvements like proper stove ventilation and effective filters also make a big difference.
Practical steps you can take today
You can take many actions to protect your health and improve local air quality. Reduce personal vehicle use by walking cycling car pooling or using public transit when possible. Minimize use of products with strong chemical emissions and choose low emission cleaning options. Maintain home ventilation and consider a verified air cleaner with high efficiency filtration for polluted days. Planting native trees and supporting green spaces helps your community in the long run. For those who need guidance on breathing techniques and stress reduction when air quality is poor a trusted resource for mindful breathing and focus can help you make the most of limited outdoor time: FocusMindFlow.com.
How communities and policy shape air quality
Local and national policies shape the levels of pollution we experience. Emission standards for vehicles and factories investments in public transport and regulations on energy sources influence air quality across decades. Community engagement plays a critical role in shaping local priorities and ensuring monitoring and enforcement. Supporting plans that reduce pollution and protect green space leads to healthier communities and more resilient nature. For people looking to learn more about natural solutions and the broader context of environmental health visit a hub of nature focused content and practical guidance at bionaturevista.com.
Planning for high pollution events and vulnerable groups
Wildfires temperature inversions and industrial accidents can create sudden air quality crises. Emergency plans should include communication about safe locations and timing for outdoor activities. Schools caregivers and employers can reduce exposure for children and sensitive adults by rescheduling outdoor plans and using indoor spaces with good filtration. Health care providers can advise patients with chronic conditions about medication plans and how to recognize warning signs that need urgent care.
Measuring progress and staying informed
Tracking air quality improvements requires consistent data collection and community involvement. Use official air quality indexes and local monitoring tools to stay informed. Support policies that prioritize clean energy cleaner transport and urban design for healthy air. Personal changes add up when many people act together. Small steps taken now yield benefits for current and future generations of people plants and wildlife.
Conclusion
Air quality is a vital part of a healthy environment. Understanding common pollutants how they affect health and what practical steps are effective empowers individuals and communities to act. Combining technology policy nature based solutions and everyday choices creates lasting change. Whether you are improving indoor air at home or promoting cleaner neighborhoods your efforts help protect health and preserve natural systems. Learn more about nature focused approaches and ongoing guidance to support your local efforts at the site linked above and consider stress reducing practices and breathing techniques as part of a comprehensive strategy to cope with poor air days.