8 Easy Sustainability Swaps for a Greener Lifestyle
8 Easy Sustainability Swaps for a Greener Lifestyle
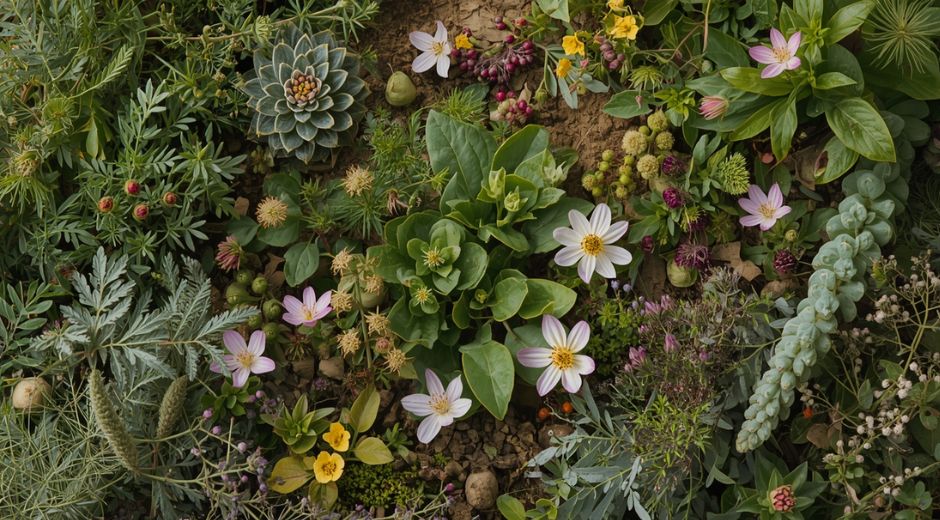
In today’s rapidly changing world, supporting local ecosystems is more important than ever. One of the most effective ways to do this is by planting native plants in your garden or community spaces. These native plants are naturally adapted to your region’s climate, soil, and wildlife, making them vital to the health and sustainability of the environment. Choosing native plants helps preserve biodiversity and reduce the need for excessive watering or fertilizers, promoting a healthier, more balanced ecosystem. In this article, we explore the top 7 native plants that can help boost your local ecosystem and contribute to biodiversity, enhancing both natural beauty and ecological resilience.
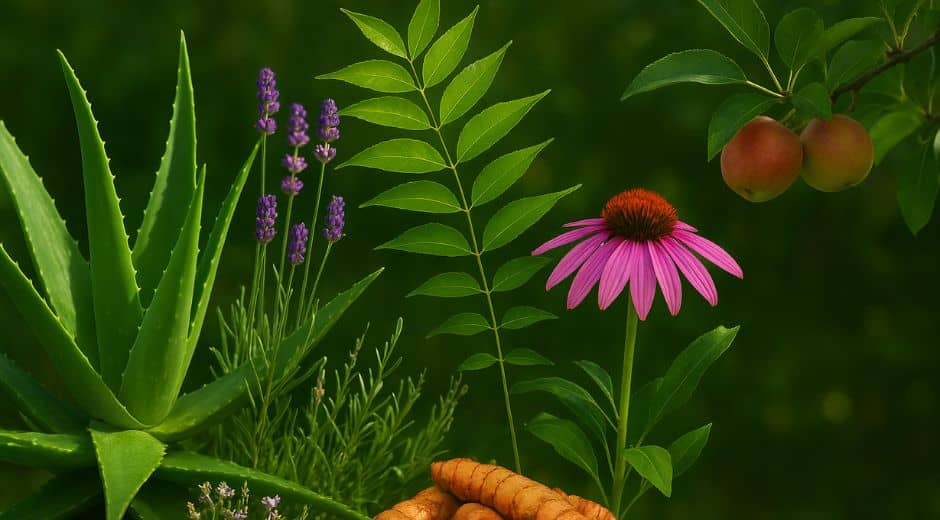
1. Purple Coneflower (Echinacea purpurea)
The Purple Coneflower is a beloved native plant known for its vibrant purple petals and resilience. It attracts pollinators such as bees and butterflies, which are essential for the reproduction of many plants. Its deep roots help prevent soil erosion and improve soil health. This hardy flower thrives in various conditions, making it an excellent choice for supporting your local ecosystem. By planting Purple Coneflower, you not only beautify your garden but also provide crucial food sources for pollinators, supporting local fauna and maintaining ecological harmony.
2. Blue Wild Indigo (Baptisia australis)
Blue Wild Indigo is a striking native plant with beautiful blue flowers that bloom in late spring. It enriches the soil by fixing nitrogen, which benefits neighboring plants. Its flowers provide nectar for pollinators, while its dense foliage offers shelter for small wildlife. Incorporating Blue Wild Indigo into your garden encourages a balanced and thriving ecosystem. This plant’s low maintenance requirements and natural resilience make it a perfect addition for gardeners seeking to promote biodiversity while minimizing effort.
3. Eastern Redbud (Cercis canadensis)
The Eastern Redbud is a small native plant tree admired for its stunning pink blossoms in early spring. It supports local wildlife by providing food and habitat for birds and insects. Its ability to grow in various soil types and conditions makes it a versatile option for restoring natural habitats and enhancing biodiversity. Beyond its ecological benefits, the Eastern Redbud adds seasonal beauty, creating vibrant landscapes that attract nature enthusiasts and promote environmental stewardship.
4. Wild Bergamot (Monarda fistulosa)
Wild Bergamot, also called Bee Balm, is a fragrant native plant that attracts a wide variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds. Its aromatic leaves have medicinal properties, traditionally used by Native Americans. This plant’s vibrant flowers and ecological benefits make it an excellent addition to any ecosystem restoration project. Wild Bergamot also helps support beneficial insects that control garden pests naturally, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fostering a healthier environment.
5. Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum)
Switchgrass is a tall, perennial native plant that plays a crucial role in preventing soil erosion. Its extensive root system helps stabilize soil and increase water infiltration. It provides habitat for birds and beneficial insects, supporting a diverse ecosystem. Switchgrass is drought-tolerant and adapts well to different environments, making it a resilient choice for ecosystem restoration. This grass also offers ornamental appeal with its graceful seed heads, contributing to the aesthetic and ecological value of gardens and natural landscapes.
6. Black-eyed Susan (Rudbeckia hirta)
Black-eyed Susan is a cheerful native plant with bright yellow petals and a dark center. It attracts pollinators such as bees and butterflies, which are critical for plant reproduction. This hardy flower also serves as food for caterpillars and other insects. Its ability to thrive in poor soils makes it a valuable asset for enhancing local ecosystems. Growing Black-eyed Susan can create vibrant wildflower meadows that support wildlife and encourage community engagement in conservation efforts.
7. Serviceberry (Amelanchier spp.)
Serviceberry is a versatile native plant tree or shrub that produces edible berries loved by birds and small mammals. Its white spring flowers support pollinators, while its dense foliage offers shelter for wildlife. Serviceberry is adaptable to various soil types and climates, making it a great choice for boosting biodiversity in your area. Beyond ecological benefits, it also provides seasonal interest and nutritional value, making it popular for wildlife gardens and natural landscaping.
Planting native plants is more than just beautifying your garden; it’s a powerful step towards restoring natural habitats and promoting ecological balance. By choosing regional vegetation and indigenous species, you help preserve biodiversity and create thriving environments for generations to come. For further inspiration and understanding of the natural world, visit National Geographic to explore their extensive resources on ecosystems and conservation.
Final Thought
Interestingly, promoting local flora also complements efforts in other fields such as sports and outdoor activities. For example, SportsoulPulse highlights how natural environments and regional vegetation enhance outdoor sports experiences and community well-being by improving air quality and scenic beauty.
At BionatureVista, we are committed to sharing knowledge and resources that empower you to make environmentally conscious decisions. Embrace native flora to boost your local ecosystem and enjoy a thriving, sustainable natural world full of life and color.
Nature Inspires Every Step

Canopy Stratification and the Hidden Layers of Forest Life
Canopy Stratification and the Hidden Layers of Forest Life

Understanding Natural Systems And Their Interconnections
Understanding Natural Systems And Their Interconnections